
🌍 Gravitation: Summary Note
Gravitation is a natural force by which every object in the universe attracts every other object. It is one of the fundamental forces of nature, responsible for keeping planets in orbit, pulling objects toward Earth, and maintaining tides.
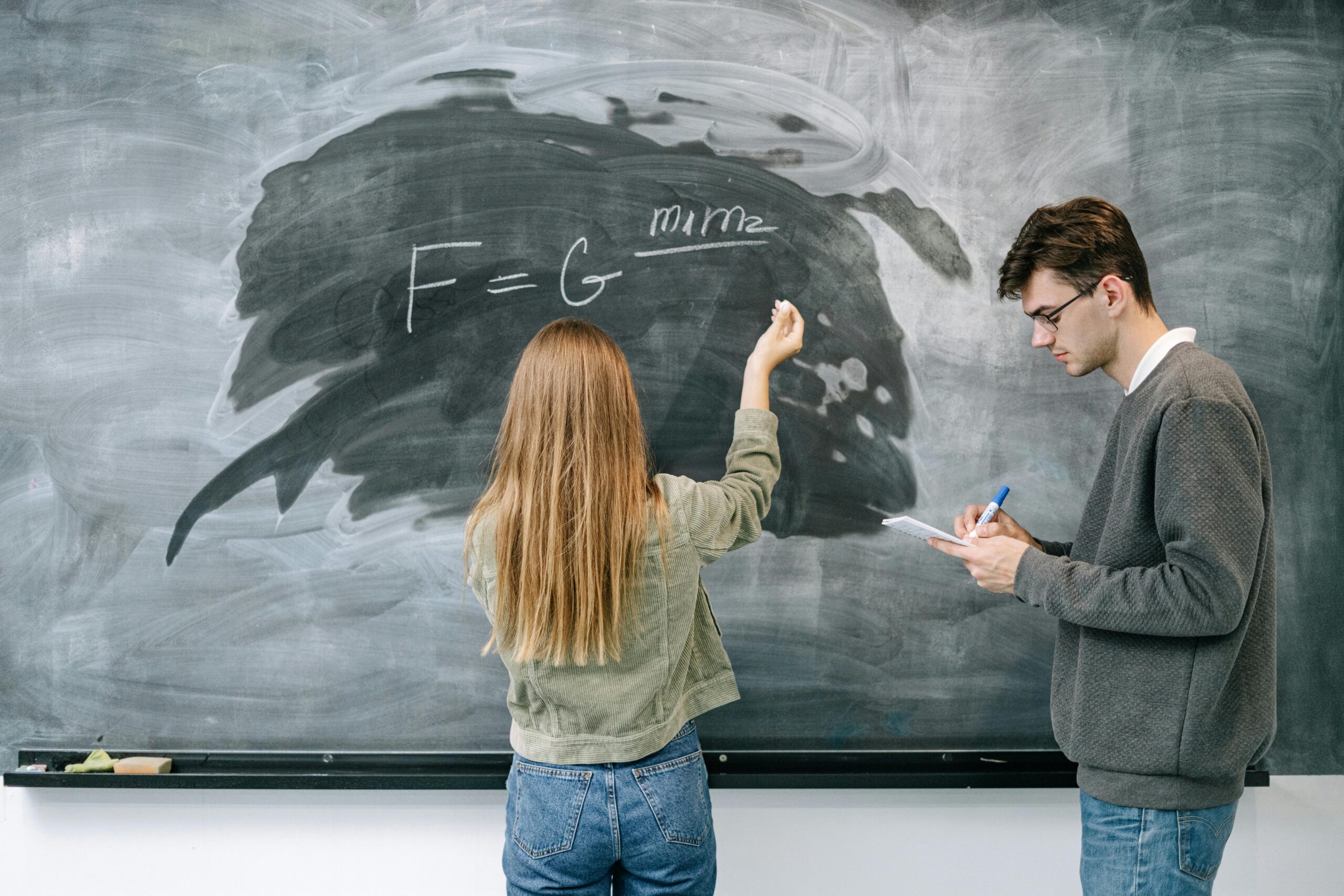
🔑 Key Concepts:
-
Gravitational Force: The force of attraction between any two objects with mass.
-
It is always attractive, never repulsive.
-
It acts along the line joining the centres of the two masses.
-
-
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation:
“Every object attracts every other object with a force directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.”F=Gm1m2/r2
Where:
-
F= gravitational force
-
G = universal gravitational constant ()
-
and = masses of the two objects
-
= distance between their centres
-
-
Weight: The gravitational force exerted by the Earth on an object.
W=mg
- = acceleration due to gravity (~9.8 m/s² on Earth)
-
Acceleration due to Gravity (g):
-
Decreases with altitude and depth.
-
Depends on the mass and radius of the Earth.
-
-
Free Fall:
-
Motion of a body only under the influence of gravity.
-
All objects fall with the same acceleration regardless of mass (in the absence of air resistance).
-
-
Mass vs. Weight:
-
Mass is the amount of matter (constant everywhere).
-
Weight is a force due to gravity (varies with location).
-
-
Orbit:
-
The path followed by a satellite or planet due to gravitational attraction.
-
Satellites are in constant free fall around the Earth.
-
🧠 Remember:
-
Gravity is what keeps us grounded.
-
It affects everything from falling apples to orbiting satellites.
-
Understanding gravitation helps explain planetary motion, tides, and artificial satellites.
Quiz Description
1. What happens to the gravitational force between two objects if the distance between them is doubled?
Hint: ✅ Correct Answer: Becomes one-fourth
🧠 Because F∝ 1/r2
🧠 Hint: Weight W∝M/R2.
So W′=600×2/(2)2 =600×2/4 =300 N
3. A satellite is revolving around Earth in a circular orbit. If the radius of its orbit is increased, what happens to its orbital speed?
🧠 Orbital speed v=√(GM/r).
As r increases, v decreases.
4. If a body is taken to a height equal to the radius of the Earth, the value of gg becomes:
🧠Hint: Since ve∝ √M, doubling mass gives √2M =√2×ve
🧠 ve=√(−2V)=√(40×106)=√40 km/s
